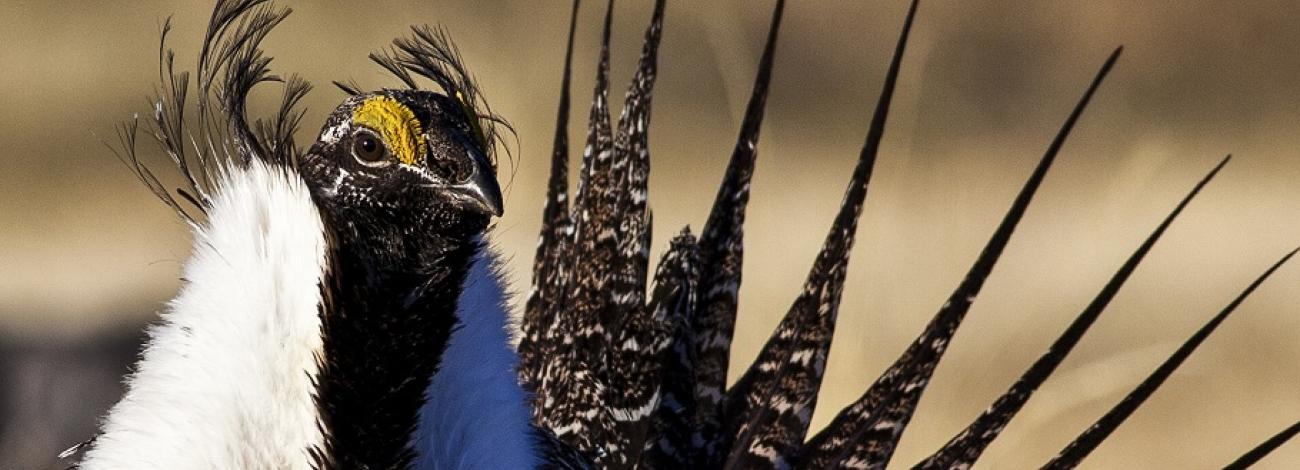
Greater sage-grouse
The BLM manages the largest single share of greater sage-grouse habitat in the United States – nearly 65 million of 145 million acres total. These same lands sustain Western rural economies built on outdoor recreation, ranching, farming, energy development and small businesses, and are critical for more than 350 other wildlife species – including pronghorn, mule deer and the pygmy rabbit. They are also the headwaters for the West's major river systems.
For decades, federal, state and private land managers have worked to conserve and restore the sagebrush ecosystem, with federal agencies managing habitat on the lands whose surface they administer and states managing and monitoring wildlife populations.
Moving forward to conserve habitat
The greater sage-grouse is in sharp decline. Populations once in the millions now number fewer than 800,000, largely due to habitat loss exacerbated by drought, increasing wildfires and the spread of invasive species.
We have announced a proposal to strengthen greater sage-grouse protections on public lands, informed by the best-available science and input from local, state and federal partners.